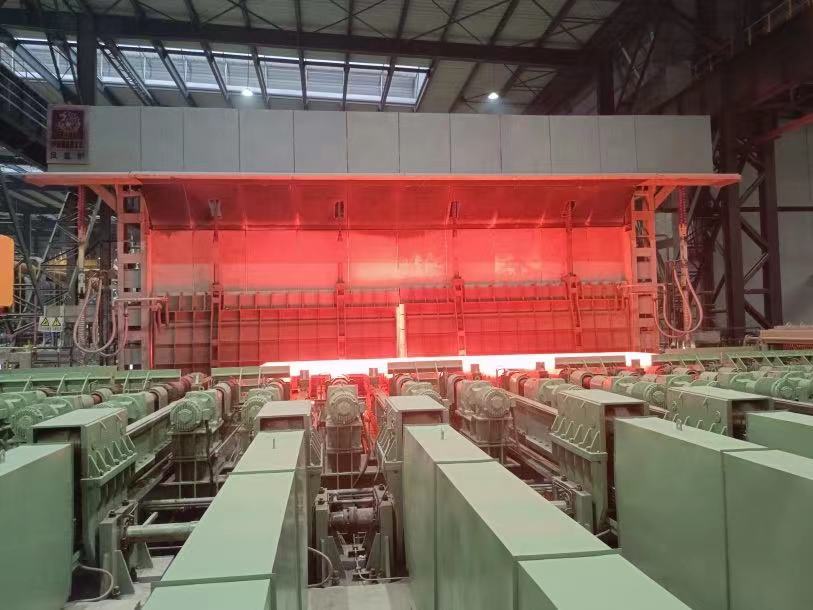
The push-steel continuous heating furnace is a thermal equipment that reheats blooming billets (plates, large billets, small billets) or continuous casting billets to the temperature required for hot rolling. The furnace body is generally elongated, and the temperature of each section along the length of the furnace is fixed. The billet is pushed into the furnace by a pusher, and it moves along the bottom slide and slides out from the furnace end after being heated (or pushed out from the side wall outlet). According to the thermal system, the temperature system and the hearth shape, the heating furnace can be divided into two-stage, three-stage and multi-point heating.
Along the length of the furnace body, the furnace is divided into preheating and heating sections, and the furnace combustion chamber is divided into a furnace end combustion chamber and a waist combustion chamber fueled by coal. The discharging method is side discharging, the effective length of the furnace is about 20000mm, the inner width of the furnace is 3700mm, and the dome thickness is about 230mm. The furnace temperature in the preheating section of the furnace is 800~1100℃。
The furnace can be divided into three temperature zones: preheating, heating, and soaking. There are usually three heating points, namely upper heating, lower heating, and soaking zone heating. The preheating section uses waste flue gas as the heat source at the temperature of 850~950℃, not exceeding 1050℃. The temperature of the heating section is kept at 1320~1380℃, and the soaking section is kept at 1250~1300℃.